#252: Jupyter is now a desktop app!
Watch the live stream:
About the show
Sponsored by us:
- Check out the courses over at Talk Python
- And Brian’s book too!
Special guest: Ethan Swan
Michael #0: Changing themes to DIY
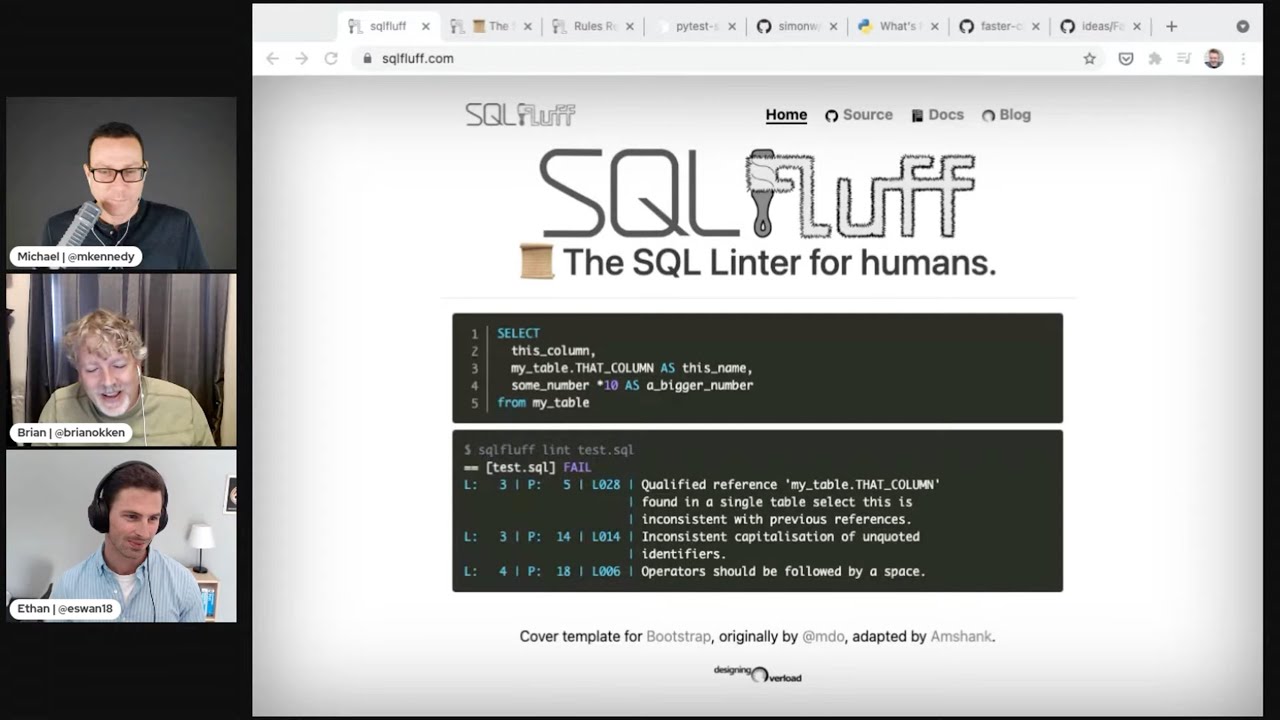
Brian #1: SQLFluff
- Suggested by Dave Kotchessa.
- A SQL Linter, written in Python, tested with pytest
- Configurable, and configuration can live in many places including
tox.iniandpyproject.toml. - Great docs
- Rule reference with anti-pattern/best practice format
- Includes dialects for ANSI, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Teradata, BigQuery, Snoflake
- Note in docs: “SQLFluff is still in an open alpha phase - expect the tool to change significantly over the coming months, and expect potentially non-backward compatible api changes to happen at any point.”
Michael #2: JupyterLab Desktop
- JupyterLab App is the cross-platform standalone application distribution of JupyterLab.
- Bundles a Python environment with several popular Python libraries ready to use in scientific computing and data science workflows.
- JupyterLab App works on Debian and Fedora based Linux, macOS and Windows operating systems.
Ethan #3: Requests Cache
- Create a requests_cache session and call HTTP methods from there
- You can also do it without a session but that’s a bit weird, looks like it’s monkey patching requests or something…
- Results are cached
- Very handy for repeatedly calling endpoints
- especially if the returned data is large, or the server has to do some compute
- Reminds me of @functools.lru_cache
- Can set things like how long the cache should last (when to invalidate)
- Funny easter egg in example: “# Cache 400 responses as a solemn reminder of your failures”
Brian #4: pypi-rename
- This is a cookiecutter template from Simon Willison
- Backstory:
- To refresh my memory on how to publish a new package with flit I created a new pytest plugin.
- Brian Skinn noticed it somehow, and suggested a better name. Thanks Brian.
- So, how to nicely rename. I searched and found Simon’s template, which is…
- A cookiecutter template. So you can use cookiecutter to do some of this work for you.
- But it’s based on setuptools, and I kinda like flit lately, so I just used the instructions.
- The README.md includes instructions for the steps needed:
- Create renamed version
- Publish under new name
- Change old one to depend on new one, but be mostly empty
- Modify readme to tell people what's going on
- Publish old name as a notice
- Now people looking for old one will find new one.
- People just installing old one will end up with new one also since it’s a dependency.
Michael #5: Django 4 coming with Redis Adapter
- #33012 closed New feature (fixed) → Add a Redis cache backend.
- Adds support for Redis to be used as a caching backend with Django.
- Redis is the most popular caching backend, adding it to django.core.cache module would be a great addition for developers who previously had to rely on the use of third party packages.
- It will be simpler than that provided by
django-redis, for instance customising the serialiser is out-of-scope for the initial pass.
Ethan #6: PEP 612
- It wasn’t possible to type a function that took in a function and returned a function with the same signature (which is what many decorators do)
- This creates a ParamSpec – which is much like a TypeVar, for anyone who has used them to type generic functions/classes
- It’s a reminder that typing is still missing features and evolving, and it’s good to accept the edge cases for now – “gradual typing”
- Reading Fluent Python by Ramalho has influenced my view on this – don’t lose your mind trying to type crazy stuff, just accept that it’s “gradual”
- Mention how typing is still evolving in Python and it’s good to keep an eye out for new features that help you (see also PEP 645 – using
int?forOptional[int]; and PEP 655 – annotating some TypedDict keys as required and others not required)
Extras
Michael
- Earsketch
- Django Critical CVE: CVE-2021-35042
- Vulnerable versions: >= 3.0.0, < 3.1.13
- Patched version: 3.1.13
- Django 3.1.x before 3.1.13 and 3.2.x before 3.2.5 allows QuerySet.order_by SQL injection if order_by is untrusted input from a client of a web application.
Ethan
- Pedalboard
- I happened upon this project recently and checked back, only to see that Brett Cannon was the last committer! A doc fix, like he suggested last episode
Brian
- Zero Cost Exceptions in Python 3.11
- Suggested by John Hagen
- Guido, Mark Shannon, and others at Microsoft are working on speeding up Python
- faster-cpython/ideas repo includes a slide deck from Guido which includes “Zero overhead” exception handling.
- Python 3.11 “What’s New” page, Optimizations section includes:
- “Zero-cost” exceptions are implemented. The cost of
trystatements is almost eliminated when no exception is raised. (Contributed by Mark Shannon in bpo-40222.) - MK: I played with this a bit.
Joke: QA 101
Episode Transcript
Collapse transcript
00:00 Hey there, thanks for listening. Before we jump into this episode, I just want to remind you
00:03 that this episode is brought to you by us over at Talk Python Training and Brian through his pytest
00:09 book. So if you want to get hands-on and learn something with Python, be sure to consider our
00:14 courses over at Talk Python Training. Visit them via pythonbytes.fm/courses. And if you're
00:21 looking to do testing and get better with pytest, check out Brian's book at pythonbytes.fm slash
00:27 pytest. Enjoy the episode. Hello and welcome to Python Bytes, where we deliver Python news and
00:31 headlines directly to your earbuds. This is episode 252, recorded September 29th, 2021. I'm
00:39 Michael Kennedy. And I'm Brian Okken. And I'm Ethan Swan. Ethan, welcome to Python Bytes. You've been
00:45 over on Talk Python, where you talked about some really cool data science stuff, and now you're
00:50 over here. So thanks for being here. Tell people a bit about yourself. Yeah, I was on Talk Python
00:54 236. So it was a while ago, but that was really cool. I work for a company called 8451. It's the
01:00 data science subsidiary of Kroger. And I'm a data scientist, but basically what I do is build tools,
01:05 mostly which are in Python, for our data science department. So we have like 250 data scientists,
01:11 pretty large department. And I build like packages and some dashboard sort of things,
01:15 just like various technology helper stuff for data science.
01:18 Yeah, it sounds really fun. And you all run what we were talking about before we hit record.
01:23 Probably one of the larger data science groups out there, right? I think of data science as being
01:28 like, there's a couple of folks that are embedded with like a marketing team or a product team or the
01:32 software development team a lot of times, but you are a properly large group of data scientists.
01:37 I mean, in theory, that's what the whole company does. So it's a very cool experience. And often,
01:42 I think that's nice for the team I'm on, because you don't usually get so many customers on internal
01:47 tools. You know, we're building stuff for literally hundreds of people to use. And it's a little bit
01:51 like releasing software externally. So it's yeah, it's a lot of fun.
01:55 Yeah, fantastic. All right. Well, we're definitely looking forward to having your insights here
02:00 for the show. Now, Brian, I do want to start off here. I want to talk about some deck staining.
02:05 Thanks. Yeah.
02:06 So because those of us who are very attentive on Twitter saw that Brian kindly responded to somebody
02:14 who sent us a message and said, Oh, I see you were talking about pallets. We should also talk about
02:18 deck stain and other DIY project resources. And maybe you could put that stupid article on your
02:24 blog. You're like, we're not a blog. We talk about pallets because it's on Flask. And then
02:29 Twitter decided, Oh, you are now classified under the home improvement category. So are we changing
02:34 our theme or what?
02:35 Apparently just me. That's most of you. I've got a few new followers now. And most of them are people
02:42 that like to make things. So.
02:43 Well, it's fun to make things as well. But maybe we'll maybe we'll talk more about SQL and stuff
02:48 like that. What do you think?
02:50 Yeah. So this, this was sent to us by Dave Cochesa. Thanks, Dave. I want to talk about
02:56 SQL fluff. So I had never heard of this, but it looks pretty cool. So SQL fluff is a Python,
03:03 a Python package that is basically a linter for SQL. So that's how interesting. I haven't really
03:10 thought about linting SQL code, but it makes perfect sense.
03:14 Yeah. Well, I mean, there, there is like, I don't really think about it too much either,
03:19 but there's like things like, should you capitalize all the keywords? And some people just like it
03:23 like that. So there is style. There's like both style guides around a SQL. I assume there's style
03:30 guides. And this lets you help, helps you enforce it. Not, not just style guides, but just, you know,
03:36 looking for mistakes and things. The, the page looks really slick for, I like the logo,
03:43 the fluff logo, but, but the, one of the things that's great about it is the documentation. So
03:48 the documentation looks wonderful. And there's one of the neat things about this is there's a
03:55 different rules or different dialects set up so that it treats different things like ANSI and
04:01 Postgres and MySQL different. And, and I'm not sure if these are, or if these are style differences or,
04:09 or, or, or what they're doing different, but, but it's kind of interesting that they'll, they'll,
04:14 there is a difference there.
04:16 Well, one of the things that comes to mind for me, if this reports errors and I suspect it probably
04:20 does, one of the things that comes to mind for me is if using like Microsoft SQL server and you're
04:24 using a parameterized query, because you don't want little Bobby tables in your school, you would say
04:30 at parameter name, whereas in with like MySQL or Oracle, it'd be like a question mark. Right. And I think
04:35 one is illegal in the other syntax. So at least in that regard, I think, I don't know for sure it's
04:41 illegal, but I'm pretty sure like it may be, and it could be that you've got to say what type of
04:46 parameterized specifications and other extensions are valid. And even, I think there's some keywords,
04:51 right? Aren't there some different keywords in some cases? So it would make sense to have to know
04:55 the dialect. Yeah. Yeah. And also like you were saying, if, if there are really are big differences
05:00 differences or even minor differences, there might be some queries that you don't run all the time.
05:05 And so you're not sure if you switch databases that they might be broken if you're trying to port. So
05:10 kind of cool. There's a list of, so it has rules, like a lot of linters, rules for failure. And I like
05:16 the rules page because it talks about the rules, but also shows you the anti-pattern and best practice.
05:23 I kind of like that style. I don't know if I like the terms anti-pattern and I really don't like the
05:29 term best practice, but nonetheless, the, what it's looking for and what you should do different is,
05:35 is a good thing to have in the documentation. It's pretty cool.
05:38 Yeah. I do like the anti-pattern aspect. I, maybe pattern. You're going to have an anti-pattern,
05:43 just have the pattern. I don't know.
05:44 I'm not sure. One of the things that's in the documentation, I can't remember where,
05:48 there it is, that people should be aware of. Supposedly this, even though it has like
05:53 1982. That's interesting. Stars. It's still in alpha phase. So there's a note here that says,
06:02 expect significant changes. So just be aware of that.
06:05 Cool. It doesn't seem major because you're not doing runtime behavior on it, right? It's a thing
06:11 you run against your code and then you look at the output.
06:13 I mean, maybe it's in your CI system or something, but. Yeah. But it's not in production. Right. So like
06:20 you are, you won't get called on a weekend because the site went down because this thing got automatically
06:26 updated or something to that effect. Yep. I guess it could have broken your, your queries, but you know,
06:31 whatever. and it's good to have an audience because, we did have a Paul from the chat say,
06:38 Ethan's correct. There are different keywords between different SQL dialects. Yeah. We use a,
06:43 Oh, sorry, Michael. No, go ahead. Go ahead. No, we, we use a lot of SQL as I would assume most data
06:47 science shops do. but one, what this made me think of was, one contentious topic in people
06:53 who write a lot of SQL is, especially when you have a bunch of column names and you're selecting
06:57 regularly, you know, five to 10 columns, the comma first, I don't know if you've seen the
07:03 approach where you do a new line, comma, column, comma, column. So it lines up really nicely and it
07:08 makes it easier to delete things. that's a very common thing that people feel strongly about.
07:13 So I could imagine linter as being very handy to at least enforce one style throughout a company
07:17 because you know, we don't have that. Yeah. Nice. And then I was going to add that Pamphil Roy on the
07:23 audience says it would be a cool if there was a plugin for D Beaver and Sam Morley asks, I wonder if it
07:30 checks if inputs are sanitized. I don't know if it should, but Paul also asks if it validates for
07:35 syntactical correctness beyond just style. He does say that it catches errors and bad SQL before it
07:41 hits your database. So I'm going to go with the yes. That's pretty cool. Yeah. Ethan, I was thinking
07:45 as I was watching Brian present this, that you probably do way more SQL than I do, even though I
07:51 run in production websites that are backed by databases, not just because there's no SQL, but
07:56 because I use ORMs and the data structure doesn't change. But for, data science,
08:02 you're kind of in a more exploratory mode, right? Yeah. I think it's pretty interesting because,
08:06 you know, like listening to this podcast, people talk about using ORMs a lot, but in data science,
08:11 you don't really think of data in that relational model as much. I mean, you can, but like thinking of,
08:16 as of rows as objects is really not common. So I feel like my relationship with databases is totally
08:21 different. My first couple of years, I was mostly writing SQL, but it was, it was literally just
08:27 asking questions for analyses, which is such a different use case than what people use it for,
08:31 for web development. Right. Yeah, absolutely. It's, it's super different, super different.
08:34 But if you were to explore data, wouldn't it be nice to have a desktop application instead of a web
08:41 browser for doing so? So Jupyter and JupyterLab have got to be the most popular way that people
08:46 interact with data on the data science side. It's certainly an exploration stage anyway.
08:50 So super big news that is old news is new again, but better. JupyterLab desktop app is a thing.
08:58 Like I can download JupyterLab. It's an icon on my doc or on my task bar. I click it,
09:04 it runs like an app, but inside of it is Jupyter notebook, like the whole JupyterLab with terminal
09:10 and Python consoles and kernels and all those things. That's cool. That's, that's very nice.
09:15 Yeah. Have you played with this yet, Ethan? No, we, so I don't know how common this is,
09:20 but I think for us, at least mostly people aren't working on their local machines. They're really
09:25 connecting to a session of Python on a remote server. So mostly what we do is we fire up Jupyter
09:31 on, on a remote server. And then from our laptops, we hit that URL to actually look at the notebook.
09:36 So I'm not sure a desktop app would work as well for us, although maybe it's, it's definitely
09:40 interesting. And I wonder if there's some native features of desktop apps that are available,
09:45 that are going to be a reason to switch.
09:46 Well, what I would say right now is it's a really nice self-contained thing. So I'll just
09:53 read the description real quick. JupyterLab app is a cross-platform standalone application.
09:58 Distribution of JupyterLab is a self-contained desktop application, which bundles the Python
10:03 environment and several popular libraries to use and scientific computing, like surely pandas and
10:09 NumPy and those kinds of things. So what you get is you get just an app that's, it's ready to go that
10:14 you could just have somebody install and you can say, here, open this notebook and run it. And long
10:19 as you're using core libraries and stuff like that, you don't have to think, okay, go to the terminal,
10:24 you know, set up the environment and then type JupyterLab. Oh, you need to activate the kernel
10:30 and you got to do this and that, you know, it's just like, it's, it's a real simple, here's, here's the
10:35 thing. No nonsense type of app.
10:37 And you lost a whole bunch of people with just open the command line.
10:40 Yeah. That's so true.
10:41 Yeah. Yeah. So you don't have to hear, right? You just, it's on your doc. You click it just like,
10:45 like you would with Word or Firefox or whatever. And it's, you're there. It starts and manages the
10:51 Jupyter server in the background. There may be a whole host of command line arguments. You can give
10:58 it to say like run, but use that server and other things along those lines or run and use this conda
11:04 environment. I didn't see any of those. And so from what I can tell is it's kind of a local version
11:10 of Jupyter. So it might be super interesting for you all in your workflow.
11:14 One place where I think this would be really handy is teaching beginners. So I actually teach some
11:19 Python, especially for data science classes at the university of Cincinnati. And one thing that
11:24 regularly is really confusing to people is that you can't double click on a notebook file and have it
11:28 open because that's such a typical experience of files on a computer, double click. And there's an
11:32 application that opens that file. Oh, interesting. Yeah. And there are workarounds. If you have
11:37 Anaconda Navigator, it kind of works, although it's, it's a little hitchy. But I would assume
11:43 that if you have a desktop app, you'd be able to register that with the operating system, whatever
11:47 that process is to say, like when I click on .ipynbs, open it. Because I find I have to teach students,
11:53 no, start up Jupyter, open your browser, navigate to that file in the browser.
11:58 Were you in the wrong folder in the terminal when you ran Jupyter? Which is, well, sorry,
12:02 you're now locked out of that tree, that, that part of the tree of the folders.
12:06 And then suddenly you're having a conversation about paths. Yeah. You go down. It really is like
12:10 something I don't like to deal with. So maybe this is what I should recommend for people when I teach.
12:14 What I would recommend is just check it out and try. So I do have a bit of a comment here from Dean
12:20 out in the audience. I like the concept of JupyterLab app, but I'm afraid it'll be a V in V in V,
12:25 V in V, virtual environment nightmare. So what I found interesting is it's discovered, you know,
12:31 when you're creating kernels for Jupyter, you have to run a command. I always forget it and always have
12:38 to duck, duck, go or search this to figure out how to do it again. But I have to get the command to say,
12:43 create this environment and then register that as, so Jupyter finds that content environment,
12:50 that V in V, right? It's IPI kernel install. I have to do this all the time.
12:55 Yeah, exactly. And I know that it's basically that, but the exact command, I always forget.
12:59 So that command, it seems like it picked up the ones that I had run previously for standalone
13:05 terminal JupyterLab. So the virtual environment story is the same as Jupyter itself without that.
13:13 I think all we're getting here is we're getting the libraries plus Python plus the server starting
13:19 all bundled together. And it's basically the same as if you just run it on the command prompt.
13:24 I think as long as was it Dean, as long as Dean doesn't want to be starting Jupyter from the virtual
13:30 environment, it should be fine. Like when you said, Michael, about the kernels, that's the much more,
13:33 I recommend people do it that way. Cause some people do like to just install Jupyter in whatever
13:37 environment they work in and launch it there. But I have a hard time imagining how that would work in this
13:42 case. Yeah, I do as well. And Dean makes the point that once you have to go and register all that kind
13:47 of stuff on you, like when you're down in the terminal doing this, you've kind of lost those
13:51 same people. And that may well be the case, but I can see, you know, this is sort of a first version
13:57 of this. I can see that those are some of the desktop things that could add, right? It could add a
14:01 setting section where you, you have a dialogue for managing these things and creating new ones and so on.
14:06 So it could be pretty neat. Yeah. Definitely something to watch. All right. Before we move on,
14:10 Paul out in the audience has a quick question for you, Ethan, a tangential one. Python has some
14:17 really great SAST tools like Bandit, but I'm not able to find good options for R. And I know that
14:23 you live in a world that does both R and Python. Yeah. Do you have any thoughts on this? I have no
14:28 ideas. I'm going to come off as a fraud, but I don't know what SAST is. I have to, I have to admit,
14:36 like what I do. I know I said, I'm, I'm a data scientist, but in some ways that's nominal.
14:40 Like really a lot of what I do is software development for the data scientists.
14:43 Data scientists are your customer in a sense, or your, your target user. Yeah.
14:48 Yeah. So I think a lot of what I hear from users is that there are certain measurement tools and
14:53 certain statistical tools that are available in R that take longer to get to Python. So I wouldn't
14:57 be surprised if that really is what's happening here, but I don't personally have any suggestions.
15:01 Yeah. Okay. Yeah. So Bandit, is like a tool that will scan for known security vulnerabilities,
15:07 like leaving debug settings on in Django. Oh, see, I was wondering if that was okay. Then,
15:12 then that I also don't know. That's a little different than what I was imagining.
15:15 Yeah. Awesome. All right. Well, since you got the floor, tell us about your first item.
15:21 Sure. So, I found this requests cache package, in a newsletter recently,
15:28 and this might be a little bit of a shorter one because unfortunately I haven't had a reason to
15:32 use it yet. but basically what this does, scrolling down here is you can instantiate
15:38 sessions just like you would with the traditional requests library. So probably, request is one
15:44 of the most commonly used Python packages, I would guess. Yeah. For anybody who's not familiar,
15:48 you use it to make HTTP requests, which is basically to bring anything back from me. And, the tagline,
15:53 I think is HTTP for humans, but it's just known for being easy to use and you can access the internet.
15:58 But one thing that I have found is that, especially if I'm, if I'm testing something in an interactive
16:04 way, not mocking, but I really want to see if my code pulls back what I expect. sometimes I rerun
16:09 the same request over and over and I say, go get this, go get this, go get this often the same data.
16:15 And sometimes that data is large. and that takes a really long time. So requests cache is a way of
16:20 creating a session object that looks and acts the same. But when you call, a get or a post
16:26 request on the same URL, what, with the same data, what you get back is actually just the cached
16:32 version of that data. so you're not waiting every time the first time you incur the network
16:37 latency. And if the server has to do anything to like compute the data, or if it's enough data that
16:42 it takes some time to get to you, you wait for that. But the second time everything runs instantly,
16:46 which is really a big advantage. So I've done some things with web scraping where I'm
16:51 building some kind of, I want to build like a function that pulls some things down and makes,
16:55 or pull some things out of that, but just waiting every time to run the function for it to
17:00 pull from several different pages and, you know, do some computation on that actually makes it pretty
17:05 slow. But if you were able to cache it like this, that'd be a lot faster.
17:08 Yeah. This is nice. I love the fact that it's just a stand in replacement for the request
17:12 session itself. Yeah. And if you scroll down a little more, it actually shows a way to do that
17:17 with the regular requests library. And this actually scares me a little bit. This is kind of,
17:21 kind of magical what's going on here. You just run a one-liner with requests cache,
17:25 and then suddenly the requests library itself works differently. So I wonder if that's a monkey
17:30 patching or what's going on. It probably is, but it is, it is really slick. so I would imagine I'll,
17:36 I'll have a reason to use this soon, but I haven't tested that yet. It does offer a lot of
17:40 configuration options. And one thing I thought was, was a good, idea to look at is an expiration
17:45 date. and that's sort of like, when should you invalidate the cache and actually pull again?
17:50 Cause you maybe should trust that the website is sending you all the same stuff today, but if you
17:53 rerun your code in a week, make sure that it still responds the same way. So it's got some nice options
17:58 like that. I really like that. That's interesting. So you could use it not even just for testing. It could
18:02 be for, actual data, but you know, it's not getting updated very often. So.
18:07 Yeah. For large data is what I was imagining. So I, yeah, like I said, there's, there's been some
18:12 times where I've like pulled things from APIs where they send back a lot of data and you don't want to
18:15 be waiting for that. Yeah. Or even you just want to make sure that, multiple calls to it are
18:20 getting the same data, even if it does change. that's true. Yeah. So keep consistency.
18:25 Interesting. This reminded me a little bit of the, I don't know if people are familiar with the
18:30 at cache, or LRU cache. It used to be another, there's a new one just called at cache in the func
18:35 tools module built into Python. And that's very, very handy once you know, it's there because often
18:40 you have a function that you don't want to recompute the work for. And this is almost like somebody
18:44 rewrote requests with cache in it, which is pretty cool.
18:46 Yeah. It's got a lot of nice features. You know, I think a question from handful out in the audience,
18:52 can it cache to redis because production in memory production caching, you could blow it up,
18:58 right? Blow up the memory. So a couple of things that stood out to me that were interesting there
19:02 was, yeah, you could throw a func tools, LRU cache decorator onto an expensive thing, which is fine,
19:10 but that's in memory, right? And plus things have to be hashable and whatnot, but you could do that.
19:14 but it's in memory. And a lot of times if you have scale out as you do on web apps,
19:19 like in production, as in, Brian was talking about, you have web farms, like five or 10 copies
19:26 of micro whiskey or something running. So then there's still five times you got to do it before
19:31 it really gets cached. And then also it goes to SQLite. So it gets stored to disc, right? So it's
19:38 not even in memory. It's, it's on disc. So like you said, there's other backends as well, but I think
19:42 having just by default going to a SQLite file with an possible expiration means you could just turn
19:48 this on and leave it expire after a day. Go tell us about the backends. There's more than just SQLite.
19:53 Yeah. It does seem like you have some options. I mean, like I said, I haven't had a reason to use
19:57 this. So I haven't toyed around with all these, but it, this, the way this is documented leads me to
20:01 believe that it really is just a drop in replacement, that you can configure what you want to use as
20:05 your backend. And I do wonder, so yeah, what you were saying, Michael, about having multiple instances,
20:09 I do wonder how that would work. Would it check to see if any of the instances had cached this yet?
20:13 would it like proactively go reach out to the cache or? Yeah. Well, I think if you have some
20:18 memory one, it's going to be a hassle, right? Like one of the options is memory. but all the other
20:22 ones, file system, grid FS, Redis, SQLite, those are all support, you know, concurrency. They support.
20:29 Yeah, exactly. So, so then it will scale across process seamlessly.
20:33 Yeah. So that, that could be actually really helpful for something like that, where you have
20:36 a distributed set of workers. Yeah. Yeah, for sure. let's see some fun stuff about your monkey
20:42 patching comment. And Dean says monkey patch is like having a real monkey. It's very cool when other
20:46 people have it, but having it in my house is scary. And yeah, Sam just, has a too much experience at
20:53 the zoo, I think, with that as well. So yeah, monkey patching is a little sketch.
20:58 Oh, nice. All right, Brian, you're up next. Okay. What do we got next? I, so I did something,
21:06 kind of dumb the other day. so I went ahead and I needed, I pushed a new package
21:14 out on PyPI. Really. I was just trying to, to remember how to, the whole process, because I
21:21 wanted to just remind myself of like, if I have something new, something cool I wanted to share,
21:26 how do I get it out there to PyPI? So I was walking through that process and I was doing it
21:30 for a plugin. You did your own typo squatting. Apparently. so I published pytest Slow,
21:37 and then, but who was it? Brian Skin said, cool, but, maybe pytest Skip Slow would be
21:46 better. And I'm like, oh man, that is a better name. cause that's what it does. It skips the slow
21:51 tests by default. So, and this is totally lifted from the pytest documentation about,
21:56 they have this example, but nobody's written a plugin for it. So I did this. It's a little tiny
22:01 thing, but so I renamed it, but how do you rename it? So I went out and searched. So how do you rename
22:07 something in PyPI? You can't really do it, but you can create another one. And then, so this is nice.
22:14 Well, who was it? Simon Willison wrote this up. It's a PyPI renamed cookie cutter template.
22:21 And I didn't actually use the template, but I did use these steps. So the steps really are create a
22:27 renamed version of the package, which I did then publish it to PyPI under the new name and create a
22:33 final release for the old name that points to the new one and, depends on it and have dependencies
22:40 so that if somebody installed the old one, they'll really get the new one. it sounds more
22:44 complicated than it is. It's just a few steps, but, there's a cookie cutter you can use.
22:49 The cookie cutter uses setup tools and I didn't want to do that, but, so I used, I did basically
22:55 copied his, the entire thing. and then he's got a demo. So if you, you look at it, so if you go to
23:02 the old one, old version, it'll just have a thing that says, Hey, I'm going to the new one now.
23:08 so I did that and, and it was neat. I really appreciate the steps. and it's,
23:15 it's all good.
23:16 Yeah.
23:16 That's cool. You can also use it for aliases. Like you can install BS for or beautiful soup for,
23:22 right. And it's kind of the same.
23:23 Oh, is that how, is that how they do that?
23:26 I I'm guessing, I don't know, but it sounds like the same.
23:29 I didn't know that.
23:31 So now, so now when I go to pytest, if you go to the old one, it just shows it's now a new name,
23:36 go to the other one instead.
23:37 So, but if I install the old one, it, it kind of just pulls in the new one.
23:41 Yes.
23:41 Yeah.
23:42 Yeah. Very cool.
23:43 Yeah. Brian, you were, you were refreshing on PyPI, but I actually just pushed my first ever
23:48 package to PyPI a couple of weeks ago. And so that was, you know, a bit of a trial, but I was
23:52 amazed at how straightforward it is. The documentation is excellent. It really is,
23:55 is pretty seamless actually for somebody who's never done it before. So who knows, hopefully I
23:59 don't make any mistakes on the one package I have and need to read. Yeah. But we'll see.
24:03 The immutability of it is a little scary, but yeah.
24:05 So for me, the hard part was just understanding that it really was pretty simple. and then also,
24:12 getting the hashes right. So you have to like, you have to get like, you know,
24:16 signatures and stuff to make sure that you can push to the PyPI correctly. So, yeah.
24:22 Yeah. But even the documentation there, it's a little intimidating, but it actually
24:25 turned out to be only a few minutes of work. So that was, that was pretty nice. Good for them.
24:28 I guess PyPI is the people to praise for that.
24:31 Yeah. So what was your package?
24:33 Oh, I, it, it's called pre-mark. It's, it's a spinoff of a JavaScript library for making
24:40 slides. And I just make a lot of slides for teaching. And I actually found, an existing
24:46 package by man. I want to, I mean, yeah, here it is. It is not ready. That's why
24:51 it's a release candidate. but I, I, yeah, I based it on this existing package by
24:57 at Tyler Dave on GitHub, and talk to him a little bit about it. He had already built a really
25:01 lightweight tool and I just expanded on it, but I like to write my slides in Markdown, which is really
25:05 what this is for. You write your slides in Markdown and a bunch of different files. It stitches them
25:09 together and creates a, what's called remark JS presentation. so I use this for my own teaching.
25:14 Nice. I'll check it out.
25:16 But it's, it really is largely a sample project to just like learn how to use PyPI and things like
25:21 that.
25:22 Yeah. Very cool. All right. Up next we have caching. Oh wait, we just talked about caching. No, I have
25:28 more caching. So Django, I have two, two pieces of news on Django. this one comes from Carlton
25:35 Gibson. I'm one of the Django guys and also, one of the hosts at Django chat, the podcast. So
25:42 they are adding a Redis cache backend to Django. So traditionally Django has shipped with Memcache,
25:51 Memcached D, that cache backend with multiple implementations, I think even. So you can go
25:57 there like Django as an ORM, it can talk to stuff. So it has a cache backend as well. And it could talk
26:02 to Memcache, but it couldn't talk to Redis. And they found that the vast majority of people are using
26:08 Redis and they said, well, why don't we have a backend for it? Well, guess what? It's going to.
26:12 So this was merged and this whole conversation here around the PR and the issue is pretty interesting.
26:18 So it starts out and says, this PR aims to support, to add support for Redis to be used as a caching
26:25 backend with Django as Redis is the most popular caching backend. Adding it to Django core dot,
26:30 the Django dot core dot cache module would be a great addition for developers who previously had to rely
26:36 on third party packages and check out how they've got this little checklist and progress.
26:40 These are the things for this PR to come along and work. So create the Redis cache class, do a pickle
26:47 serializer, et cetera, et cetera. Waiting for this other task. Here's some open-ended documentation.
26:51 So I don't think I've seen this really before, like this project tracking in the PR.
26:57 I like it's really cool.
26:58 Yeah, I do too. The other thing to note that this came in on May 23rd and there's a
27:03 large conversation. If you go there, there's 30 pages of conversation about it and you can see
27:09 it evolving. Like, okay, we finally got the test pass and we finally got it implemented. Now let's
27:13 move on to the documentation now, et cetera, et cetera. And then finally, boom, September 15th,
27:19 that's three, three and a half months, something like that. It's closed. So you can actually sort of
27:23 track what the Django team is doing for adding features, like core important features to Django.
27:29 It's always so interesting to watch open source communities like this, especially on somewhat
27:34 contentious issues where people disagree and how they manage these things. I think it's really
27:38 impressive because a lot of teams that even meet in person regularly in our small teams still struggle
27:43 with that kind of stuff, but these huge open source projects manage it. Somehow they implemented the
27:48 feature at the end. So pretty impressive.
27:49 Yeah, absolutely. It's very impressive. Also, I said this was from Carlton. He participated a lot. I'm not 100% sure that he was the originator. This might be Daniel Abasi. So sorry if I misattributed credit there, but for whoever did this, the original issue, I think Carlton had put up. So I'm not sure who was really sort of the initiator there, but I think it's cool. And it's also neat how out in the open, this whole thing is.
28:16 Yeah. Putting the open in open source.
28:19 That's right. Hi, Brian. What you got?
28:21 It's me again. Are we done with our things?
28:26 All right. No, I think I got one more.
28:28 Oh, no, sorry. I totally, I was for some reason in wrong order. Yes, Ethan, you're up next. Sorry.
28:33 Totally fine. So yeah, so I wanted to highlight PEP 612. So I happened upon this, I forget, there was some other PEP I was looking at and they'd linked off to this one.
28:44 But a little bit of background. A PEP is a Python enhancement proposal. It's basically like how ideas are proposed in terms of what to do with Python as a community or as a language.
28:54 And I recently have been really kind of diving into type hinting Python. So there's a surprising number of PEPs about type hinting. And what this one does is something I guess I didn't really realize I needed.
29:05 It was a bit of an annoyance, but I didn't realize there was a fix coming.
29:08 Basically, what it comes down to is quite often you write functions that take in a function and return another function. So there's this example.
29:18 And this, where's the first case where they use it? I think here, param spec. I'll find it while I talk about this.
29:26 But basically...
29:28 A lot of decorator time, yeah.
29:29 Yeah. What you do with decorators is you write functions that take in other functions and return a function that has the same signature, which is to say it takes in the same parameters of the same types and returns the same return type.
29:42 It may have some other modifications of the function, but that's very frequent.
29:45 And so sometimes what you want to say is my decorator, if I want to type the decorator, say what types of things it takes in, it takes in something that is essentially a generic function type.
29:55 Any kind of function is fine that takes in any parameters and returns any return type, as long as it returns the same thing.
30:02 So it's like generics, which you would do with type bars.
30:05 But in this case, you create something called a param spec, and then you pass that as the...
30:14 Oh, man, I lost it where it is in here.
30:15 Oh, here we go. This is what I wanted.
30:18 So you pass it as the type of callable when you type the function that's taken in, and then you say you're returning a callable with the same parameter specification.
30:27 This P is a parameter specification.
30:30 And you make essentially your callables generic on both this parameter specification and on the return value.
30:38 So I know there's a lot to that.
30:40 And I think for people who are typing everything every day, maybe this doesn't seem terribly pertinent.
30:46 What I do, I said I write a lot of Python packages for people to use, and it's important both for quality control and so people know what the return values are and what they should pass into functions to have a lot of typing.
30:57 But really, what this got me thinking about a little bit is just that the Python typing ecosystem is still really evolving.
31:03 Like for somebody who's not super close to following it, it appears that like this is how Python works now.
31:09 And maybe it's always been this way, but it really hasn't.
31:12 And there's a lot of holes in how it works.
31:14 There was no way to do this before.
31:15 And this isn't finished yet.
31:16 This is a pep, but it isn't implemented.
31:19 And so right now, you don't have a way to do typing for this particular feature.
31:22 And that...
31:23 Yeah, flowing type information through different things.
31:27 That is something we haven't done a lot of in Python.
31:29 But as you called out generics and templates, that's like all you do.
31:32 That's the bread and butter of those things.
31:34 Yeah.
31:35 And it's the same idea, but features that aren't there yet.
31:37 So it's just kind of interesting to remember that this stuff is still being added.
31:41 Keeping an eye on when this stuff comes in, it can really make things easier.
31:45 And in the meantime, don't lose too much sleep not being able to type certain things.
31:49 If you can't type it perfectly, that's okay.
31:52 I've actually been reading Luciano Romajo's book, Fluent Python.
31:55 And he makes that point really well, that Python isn't a statically typed language.
32:00 And you shouldn't get too carried away trying to type things.
32:02 As much as is possible, it helps you is worth it.
32:05 But you shouldn't be religious about it.
32:06 Right.
32:07 But if you are building tools and you put this into there eventually.
32:11 Yeah.
32:11 It might help other people who consume your libraries.
32:14 It might help the editors give better autocomplete and error checking and stuff.
32:18 And we catch bugs all the time.
32:19 So as much as is feasible, I think it's totally worth it.
32:22 And actually, there's a couple other peps on that note of things still changing.
32:26 There's a couple other peps that are worth looking at.
32:28 There's a new, more convenient way to write optional types.
32:31 So right now you can say, I know.
32:33 Oh my gosh.
32:35 I've wanted this for so long.
32:37 Yes.
32:37 Yeah.
32:38 So you have to say optional left bracket.
32:40 Then the thing that is optional.
32:41 And then right.
32:42 Like optional bracket string or optional bracket user or whatever.
32:45 Yeah.
32:45 And you got to import optional.
32:46 Don't forget that.
32:47 Yeah.
32:47 That's true.
32:47 You got to import it too.
32:48 And so now there's, there's a, a pet proposing that you could just put a question mark, which
32:52 I guess isn't a problem for the parser, which is pretty nice.
32:55 This one also is in process.
32:57 Maybe this was something that was needed.
32:59 The peg parser, which recently went into, what was that?
33:02 Three, nine, right?
33:03 Where it couldn't do it before, but maybe that's a good point now.
33:05 But yeah, I, you know, they have that in C# and they have that in Swift.
33:09 And I just love like this thing, question mark, right?
33:12 Rather than a null check or specifying into question mark rather than optional bracket of
33:17 int.
33:18 It's just clear.
33:18 I didn't know that was in other languages that, okay.
33:20 That makes a lot more sense.
33:21 And it's phonetic, right?
33:22 Like if it's, if it's an int, you just say int.
33:25 If it's a question mark, it's int, right?
33:27 So you can even just like speak it out really well.
33:29 Like int?
33:30 Maybe.
33:30 Okay.
33:30 That could be null.
33:31 Maybe.
33:31 Could be none.
33:32 That's not obvious to me.
33:34 Really?
33:35 Oh, interesting.
33:35 I feel like that's a nice, a nice syntax, but maybe it isn't.
33:38 Who knows?
33:38 Maybe that won't get approved.
33:39 Yeah.
33:40 I think, I think it may not, but I do, I do hope it does.
33:43 I mean, it's the question mark.
33:44 There's an int or is there, right?
33:45 Like, is it there?
33:46 You're not sure.
33:47 Like there's, there's some subtle symbolism there.
33:50 See, I prefer the int or none.
33:52 I like that as well.
33:55 I agree.
33:55 Yeah.
33:55 That's not bad.
33:56 Now that that's more convenient to write, but that's what, that's only 310.
33:58 And the other languages that support this, and I don't know, I didn't read that PEP well
34:01 enough to know, there's a runtime behavior, not just a type specification behavior.
34:06 So I could say X equals like user question mark dot name.
34:12 It'll either, if the user is none, the name is none, or it'll follow down that, that path
34:17 and say, okay, user's not none.
34:18 So then I'll say dot name.
34:19 Oh, that avoids the none type has no attribute.
34:22 Yeah.
34:22 Yeah.
34:22 Exactly.
34:22 That's really nice.
34:23 Yeah.
34:23 Wow.
34:24 Very cool.
34:25 So, Will is, in the chat and he's got, Oh, I did the wrong one.
34:31 I love that.
34:32 Hey, Will.
34:35 That was pretty good.
34:37 All right.
34:38 And then Ethan, you want to tell us about one more before we wrap it up?
34:41 Oh, just another pep.
34:42 Yeah.
34:42 I, just another thing that is potentially changed how typing works.
34:45 There's right now, there's no way to specify if you've used a type dict, which is to say,
34:49 a dictionary with some keys having certain types.
34:53 there was no way to specify what, what keys were optional and which ones weren't.
34:59 You'd either say they were all optional or they were all required and there was nothing
35:02 in between, but there's also a PEP to do that.
35:04 So just, there's a lot of stuff on the horizon to keep an eye out for.
35:07 And these three peps, I think are a good reminder of that.
35:09 Yeah.
35:10 Yeah.
35:10 Yeah.
35:11 Very cool.
35:11 All right.
35:12 Now, now can we throw it to you, Brian?
35:14 Yeah.
35:14 Yeah.
35:14 Now, so this was, this is a suggestion by John Hagan.
35:18 And I just thought I'd throw it in as a, as a, an extra, just one extra.
35:23 So there, we've talked about, the effort at Microsoft and Guido and others, to make
35:28 Python faster.
35:29 and, like there's a, a whole bunch of ideas up on, on a, in the faster C
35:36 Python ideas.
35:37 and in one of this links to a couple of slide decks, talking about the making C
35:43 faster or making Python faster.
35:45 And, one of the things is a slide deck from Guido in, in it, he mentions, various
35:52 other optimizations like maybe zero overhead exception to handling.
35:55 Well, that's neat because that's already in three 11.
35:59 So in three 11, we have, Mark Shannon implementing, zero cost exceptions.
36:06 so if, if, if you have a try statement that doesn't, doesn't catch anything, there's
36:12 no cost to it.
36:13 So that's, that is very cool.
36:14 I did a little playing around with this idea and I wrote a program here that calls
36:19 string upper, like a hundred million times in a loop.
36:22 And it does that also in a try except block with no errors.
36:26 And, and so my understanding of this was that it will make entering the tri block in the case
36:32 there's not an exception cheaper.
36:33 and I ran it a hundred million times and I got, you know, not exactly the same, but it's
36:39 really similar.
36:40 But one of the other things, which I'm not doing in my example here, this is a gist
36:44 I'll, I'll put it in the show notes.
36:45 The looking into this comment, Brian is they talk about the number of the, basically the
36:52 size of the call stack.
36:54 And some of the other things, that happen in there about not pushing the exception onto
36:59 the call stack or something, unless it actually happens and those kinds of things.
37:03 So it's supposed to make function calls faster as well.
37:05 So even if my little example wasn't necessarily faster, maybe, maybe something else, there's
37:10 maybe other situations where it is nice.
37:12 Yeah.
37:13 Cool.
37:13 Ethan, anything else you want to just throw out there for people?
37:16 Well, one thing I did want to mention real fast about, about the zero cost exception handling
37:21 is I think it's always tough to teach people about try except blocks and then introduce to
37:25 them that they're actually pretty slow, especially if you use them in a function that gets called
37:28 many times.
37:29 And to be honest, I don't know the reasons for the internals being like that.
37:32 so it's really nice to feel like that might not be true anymore because they're a
37:35 good practice to have, to be able to say like, yeah, be careful, when you write code, especially
37:39 for people like data scientists who aren't day-to-day programmers to say like, oh, it's good practice
37:44 to use these and you shouldn't have to worry about performance.
37:45 So glad to see that.
37:47 Yeah, absolutely.
37:47 And just following up on that real quick.
37:50 if you look at the issue underlying this, where was it?
37:55 This is the right one.
37:56 Yeah.
37:56 They, there's an issue that's linked in the show notes and it actually shows you the disassembly
38:01 into bytecode of what it currently is and what it, it's going to be.
38:06 And it's really, really similar.
38:08 So you can see currently it does like a, the first thing it does is set up a finally and
38:13 then, stuff right at the beginning, but now just do like a no op and then do a return
38:18 value in the good case.
38:19 Otherwise it'll do a push exception and then work with it and so on.
38:23 So it, it pushes off some of the bytecode operations that add like to the call stack, like pushing
38:29 things onto it and so on at the C eval.c level of CPython.
38:34 Yeah.
38:34 Oh, that's very cool.
38:35 Yeah.
38:36 Well, the one thing I wanted to mention, well, I don't know if people have heard of
38:41 pedal board.
38:41 I think Spotify just announced this recently.
38:43 It's, it's basically a Python package that lets you do some things that you might usually
38:46 do using an audio editing tool and it's cool on its own.
38:49 but I had just listened to, I forgot if it was last week.
38:53 So the weeks before episode where Brett Cannon was on, on Python bytes.
38:57 And he talked about how, you know, anytime you see an issue with documentation, just put
39:02 in a pull request.
39:03 Most of the time it'll get accepted.
39:04 And, and he said he's, he's contributed to like 200 or 300 repositories that way.
39:09 So I found this last week.
39:10 And then in this week I was thinking about what I wanted to talk about on the show.
39:13 So I went back to this link and, lo and behold, the last, the last commit was made
39:17 by Brett Cannon and it's removing a stray back tick in the read me.
39:21 So he really practices what he preaches.
39:23 so he seems to be very active.
39:25 He's one of only, nine contributors to this and probably the rest work at Spotify.
39:29 So good for him.
39:31 Nice.
39:31 Yeah.
39:32 That's fantastic.
39:32 Nice to, for that, a little bit of real time follow-up.
39:35 Fantastic.
39:35 All right.
39:36 So I have a few extras and again, I have my, my, banner for extras, extras, extras.
39:41 So, a couple of things here.
39:43 Let's talk about something that Kelly Schuster-Perdes talked about, you know, she and Sean doing
39:50 the, teaching Python podcasts and they're doing great work over there.
39:54 So one of the things that she found for teaching is this thing called ear sketch.
40:00 You probably haven't heard of this.
40:01 I'm guessing.
40:02 So ear sketch is a project from Georgia tech that teaches coding, but through like a DJ
40:09 type of experience.
40:11 She's got a cool video up there.
40:12 It says five minutes and four lines of code.
40:14 And I got this up there going.
40:16 So, yeah.
40:17 Thanks Tony for pointing that out.
40:18 So here I'll just play what she created for everyone real quick.
40:32 People are teaching.
40:34 I want to get folks involved through music and Python.
40:37 That's a real cool project that ear sketch.
40:38 And I told you good stuff about Django before.
40:41 Let me tell you some bad stuff.
40:43 Oh no.
40:43 You might, you might meet little Bobby tables in the Django ORM.
40:48 If you're, running query set order by, and passing some piece of user input into
40:57 what you might be ordering by, you might be ordering by back tick, semi colon drop table
41:03 --or something like that, which you wouldn't want to.
41:05 So basically there's a SQL injection vulnerability in Django.
41:09 What is it?
41:10 320 up to 325 and 300 up to 313.
41:17 But yeah, less than that, right?
41:20 Less than 325 and less than 313.
41:22 So if you have those, you definitely want to patch it straight away.
41:27 That's a critical vulnerability.
41:28 So check that out.
41:30 And also that's on untrusted input.
41:32 Yes, that is untrusted input.
41:35 Don't freak if you're not taking, what would you like to sort by?
41:38 Please type here.
41:39 But still, you know, it's easy enough to just do a GitHub update, just an update to the requirements.
41:47 Now, if you're on, your code is on GitHub and this is the requirement, you pinned your version,
41:52 you probably have already gotten this as a security announcement and an email sent to you.
41:58 Yeah, that's such a nice feature.
41:59 It is such a nice feature.
42:01 But if you don't pin your version, they're like, well, you're on the latest version.
42:03 You're good, right?
42:04 You won't know.
42:04 So it still may slip through.
42:06 All right.
42:07 Yeah.
42:07 And Chris May on the live stream has some philosophical thoughts for us.
42:11 He says sometimes he doesn't even trust his own input.
42:13 Yes, we all, we've all been there.
42:15 Chris, don't inject yourself.
42:17 All right.
42:19 Shall we wrap this up with some laughs?
42:21 Yes.
42:23 Brian, this is going to take some role-playing again.
42:25 A nice little cartoon for us.
42:26 This is QA101.
42:27 Speaking of the CVE I just spoke about, and, you know, if you fix a minor bug,
42:33 you might get credit, like, whatever.
42:34 We fixed a little tiny bug, right?
42:36 Formatting a log file.
42:37 If you fix a critical bug, like, wow, that seems super important.
42:41 You've been doing good work this week, right?
42:42 So here's two developers in an open office sort of space.
42:46 Brian, you be the guy.
42:47 I'll be the woman developer.
42:48 Okay.
42:49 Which priority should I give this bug?
42:51 Well, is it easy to fix?
42:52 Yep.
42:53 I'll fix it immediately.
42:55 Critical.
42:56 Critical.
42:57 Finding the correct bug priority is key, they say.
43:00 So very nice.
43:01 I'll link to that little cartoon in the show notes.
43:03 I don't get it.
43:04 Because you're going to get more credit for fixing critical bugs.
43:08 And if you can fix it right away.
43:09 Yeah, it looks like you did way more work.
43:10 You did so much more work.
43:12 Brian over there only fixed, like, medium bugs.
43:15 Ethan and I took out the critical.
43:17 Exactly.
43:18 You do your T-shirt sizing after you finish.
43:19 After you take all the work, you assume everything you took was a large.
43:23 Yeah.
43:24 So, yep.
43:26 Exactly.
43:26 I keep asking people, so what are the points equal in hours?
43:30 No, we can't talk about that.
43:32 Okay.
43:32 Do I use powers of two?
43:36 What do I do?
43:36 Yeah.
43:37 Anyway.
43:38 Cool.
43:38 Well, thanks, Ethan, for coming on the show.
43:40 It was fun.
43:40 Yeah, this was great.
43:41 Thanks for having me.
43:42 Yeah, it's been fantastic to have you here.
43:44 Thanks for being here.
43:44 Brian, thanks as always.
43:46 Thanks.
43:46 Bye, everyone.
43:47 Thanks for listening to Python Bytes.
43:49 Follow the show on Twitter via at Python Bytes.
43:52 That's Python Bytes as in B-Y-T-E-S.
43:55 Get the full show notes over at Pythonbytes.fm.
43:58 If you have a news item we should cover, just visit Pythonbytes.fm and click Submit in the nav bar.
44:03 We're always on the lookout for sharing something cool.
44:05 If you want to join us for the live recording, just visit the website and click Livestream
44:10 to get notified of when our next episode goes live.
44:13 That's usually happening at noon Pacific on Wednesdays over at YouTube.
44:17 On behalf of myself and Brian Okken, this is Michael Kennedy.
44:20 Thank you for listening and sharing this podcast with your friends and colleagues.